SocialNetworkSimulator
Social Network Simulator
SocialNetworkSimulator, A software that enable spatio-temporal social network analysis and simulation, is co-direcetd by Xinyue Ye at New Jersey Institute of Technology and Ming-Hsiang (Ming) Tsou at San Diego State University. This tool is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1416509. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Currently, social media has been playing an important role in the process of information diffusion. Exploring the pattern of message propagation on social network help us better prepare for natural disasters or human crises. So, we developed models, algorithms, and tools to generate simulated networks, analyze simulated networks, and simulate information diffusion on social network over time.
Please cite the following relevant papers:
Ye, X., Dang, L., Lee, J., Tsou, M. H., & Chen, Z. (2018). Open source social network simulator focusing on spatial meme diffusion. In Human Dynamics Research in Smart and Connected Communities (pp. 203-222). Springer, Cham.
Ye, X. & Liu, X. (2018) Integrating social network and spatial analyses of the built environment, Environment and Planning B. doi: 10.1177/2399808318772381
Ye, X., Sharag-Eldin, A., Spitzberg, B., & Wu, L. (2018) Analyzing Public Opinions on Death Penalty Abolishment. Chinese Sociological Dialogue. doi: 10.1177/2397200918761665
Wang, Z. & Ye, X*. (2017) Social Media Analytics for Natural Disaster Management. International Journal of Geographical Information Science doi: 10.1080/13658816.2017.1367003
Lee, J., & Ye, X*. (2018). An Open Source Spatiotemporal Model for Simulating Obesity Prevalence. In GeoComputational Analysis and Modeling of Regional Systems (pp. 395-410). Springer, Cham.
Wang, Z., Ye, X, Lee. J., Chang, X., Liu, H., & Li, Q. (2018) A Spatial Econometric Modeling of Online Social Interactions Using Microblogs. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2018.02.001
Install with command prompt
In software_and_packages folder: 1) Python 2.7 64 version is required
* a. Double click *python-2.7.13.amd64.msi* to install python 2.7 64 version.
* b. Follow steps below to set the path variables in the environment variables.
- (1) Right-click This PC, and then click Properties.
- (2) Click Advance system setting.
- (3) Click Environment variables.
- (4) Go to the above location and change the Path variable.
- (5) If you install python at C:\Python27, add the following paths to Path variable. Otherwise you need to change the path according your actual path.
* i. C:\Python27\
* ii. C:\Python27\Lib\
* iii. C:\Python27\Scripts\
2) Double click PyQt4-4.11.4-gpl-Py2.7-Qt4.8.7-x64.exe to install PyQt package.
3) Double click vcredist_x64.exe to install it.
4) Install module numpy, matplotlib, Snap, and xlrd.
- a. Open command prompt and change path to the location where packages are. Here you are supposed to extract the tool file to C:\SocialNetworkSimulator. Use the command:
cd C:\SocialNetworkSimulator\softwares_and_packages
to change the path.
- b. Execute the following commands using command prompt.
```
Pip install numpy-1.13.1-cp27-none-win_amd64.whl
Pip install matplotlib-2.0.2-cp27-cp27m-win_amd64.whl
Pip install prettytable
Pip install xlwt
```
- c. Unzip snap-4.0.0-4.0-Win-x64-py2.7.zip
- d. Execute the following commands using command prompt.
```
cd snap-4.0.0-4.0-Win-x64-py2.7
python setup.py install
``` 5) To start this software, please use the command for command prompt, for example: ```Python C:\SocialNetworkSimulator\ SocialNetworkSimulator.py```
Install with Anaconda
1) Create python environment with Anaconda: * a. Execute the following commands using Anaconda command prompt.
```
conda create --name python4SNS python=2.7
conda activate python4SNS
```
2) Install PyQT4,SNAP and third party library * a. Download whl file from https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#pyqt4.
Execute the following command using Anaconda command prompt.
```
pip install PyQt4-4.11.4-cp27-cp27m-win_amd64.whl
```
to install PyQT4.
* b. Unzip snap-4.0.0-4.0-Win-x64-py2.7.zip
* c. Execute the following commands using Anaconda command prompt.
```
cd snap-4.0.0-4.0-Win-x64-py2.7
python setup.py install
pip install xlrd numpy matplotlib prettytable
```
Getting Started
After starting the software tool, you can see there is a menu bar on the top of the main window. Below is the summary of the functions in the menu:
| Menu | Description |
|---|---|
| File->Exit | Exit the software |
| Network->Generate Single Simulated network | Generate a simulated network based on a single model. |
| Network->Generate Complex Simulated network | Generate a complex network based on one or more network model. The complex network is constructed by adding edges among several smaller networks |
| Network->Save Network | Save the current network as a txt file |
| Network->Load Network | Load a network from a txt file |
| Analysis->Network Analysis | Perform network analysis |
| Community->CNM | Conduct community detection with CNM algorithm |
| Community->GirvanNewman | Conduct community detection with GirvanNewman algorithm |
| Simulator->User Level | Simulate information diffusion on the user level |
| Simulator->City Level | Simulate information diffusion on the city level |
| Data | Provide some functions to prepare the data used in the software |
Example
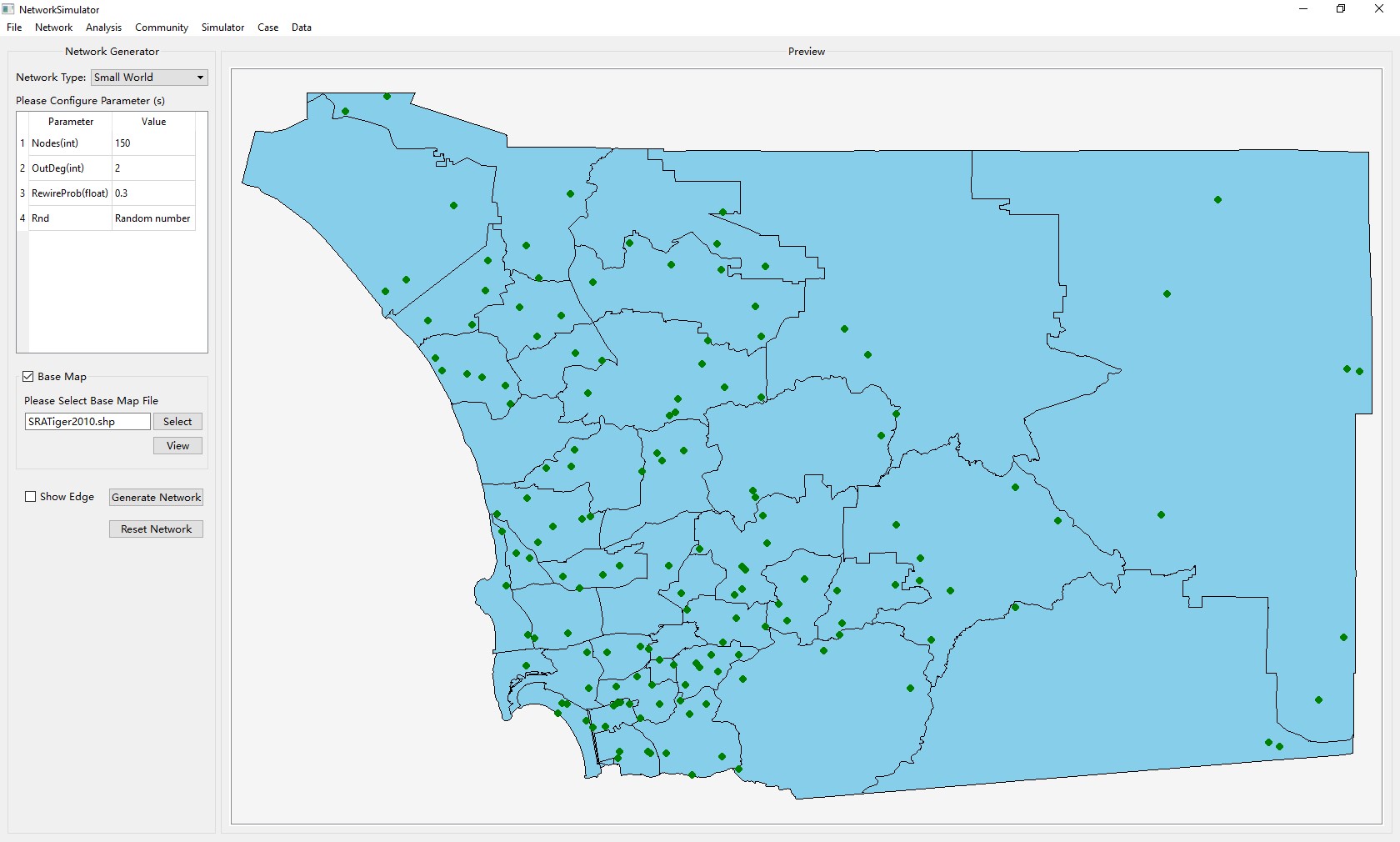
Let’s generate a single simulated network use this software.
After starting the software, the default window is for generating a single simulated network. If you are not on the interface, please choose Network->Generate Single Simulated Network to switch to the following window:
 To generate a single network, please follow these steps:
To generate a single network, please follow these steps:
- Select a network model from the pull-down list.
- After selecting a network model, the responding parameters will load automatically. Different network model has different set of parameters. Please configure all the parameters as the picture shows below:
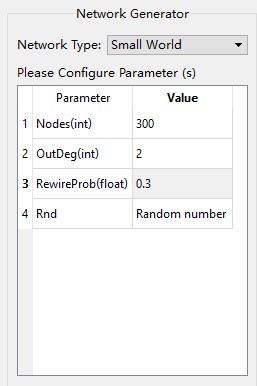
- Check Base Map to generate a network with a underlying base map (.shp file), or leave it unchecked to get a network without any base map. Check Show Edge or not to control if the network shows edges among nodes.
You may get the similar network like below: